Designated Investigative Organization services for the Act on Electronic Signatures and Certification Business
The enforcement of the Act on Electronic Signatures and Certification Business (e-Signature Act) in April 2001, created a legal framework that allowed electronic signatures to be used in the same context as handwritten signatures and seals. The Japanese government has introduced a system to accredit Specified Certification Businesses conforming to certain criteria.
In 2003, JIPDEC became a Designated Investigative Organization for the e-Signature Act. JIPDEC investigates whether the equipment of the Specified Certification Business and their implementation methods conform to the standards specified in the e-Signature Act. JIPDEC provides information provision, advice, and other support services in response to inquiries and consultation from entities conducting the Specified Certification Business, and the users of those services.
Why e-signatures are needed
Electronic signatures are being used more and more
In recent years, electronic signatures (hereinafter called "e-signatures") are being used more and more in various aspects of life cycle of a company, such as in the certification for articles of incorporation, bidding, contracts and agreements, patent applications and tax payments.
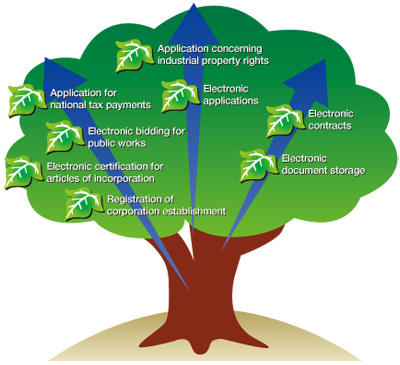
Fig. The various aspects of using e-signatures in a life cycle of a company
Many electronic certificates are issued for various purposes apart from accredited certification business.
What are electronic signatures?
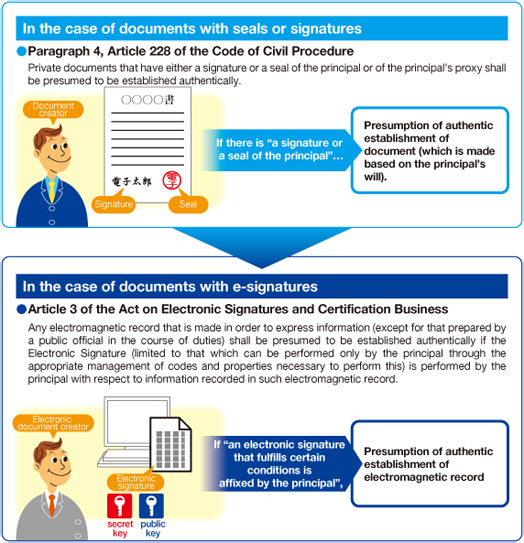
By using procedures and transactions via the Internet, the acceleration of work and paperless work can be expected. On the other hand, the use of e-signatures could lead to spoofing, falsification of data, and other problems. E-signatures are measures for addressing such threats.
Electronic documents with e-signatures can now be regarded equivalent to sealed or signed documents by the Act on Electronic Signatures and Certification Business (generally known as the e-Signature Act).
Following is a list of example services achieved by electronic contracts. Recently, cloud-based services are also increasing
Use case and use method
Digital Signature is Widely Used in Various Fields
As a result of the progress of the information society, digital signatures are increasingly being used. The use of IT in the government and government agencies, in particular, has been spreading rapidly. Widespread use of digital signatures is not limited to the relationship between the government and government agencies in the public sector. Companies entering into electronic contracts have been increasing. Since digital signatures not only reduce the time to deliver contract documents and reduce space for storing them, but also enable managing the progress of contract procedures and project information on contracts collectively, they are also being used more and more in B-to-B transactions or B-to-C transactions.
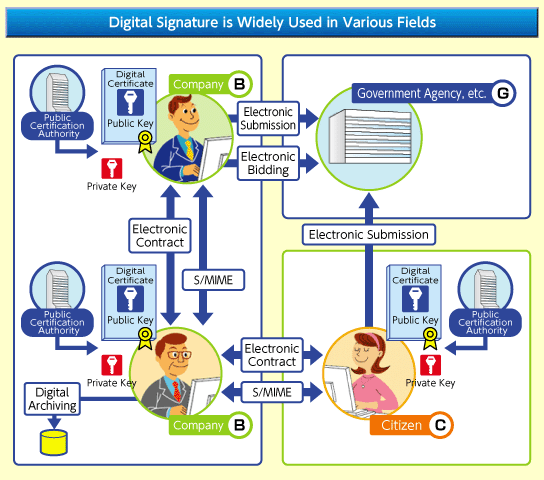
Examples of Digital Signature Usage
1. Electronic Contracts
With conventional written contracts, the legitimacy and authority of contracts were secured by signatures and stamps affixed by both parties on created contract documents. With electronic contracts, such procedures for written contracts are performed electronically. Adding digital signatures on electronic documents (written contracts) can achieve a secure electronic contract. The establishment of "the Act on Electronic Signatures and Certification Business" and "the Law concerning the Refinement of Relevant Laws to Use Information Telecommunication Technology in Connection with Delivery of Documents" has authorized using IT for written contracts and other documents. Due partly to significant benefits for companies, using digital signatures to conclude electronic contracts is increasing every year.
- Not necessary to pay stamp duties
- More efficient operation (reduced time to deliver contract documents, reduced space for storing contracts, etc.)
- The progress of contract procedures and project information on contracts are collectively managed.
- Past contracts can be easily searched for and viewed.
- Effective business continuity measures through data backup
Following is a list of example services achieved by electronic contracts. Recently, cloud-based services are also increasing
Delivering electronic contracts
Since both parties add digital signatures on electronic documents, contract documents can be securely delivered.
Searching for and viewing contracts
After concluding a contract, each party can individually search for and view it.
Delivering electronic contracts
The originals of electronic contracts are saved
The Electronic Books Maintenance Act requires one of the following measures to be taken to save the originals of electronic contract documents. In addition to electronic contracts, the same measures are also required for, purchase orders, invoices, receipts, quotations, bills, and other information on electronic transactions
(1) A digital signature (that uses a digital certificate issued by a certification business operator approved by "accredited certification business", or that uses a digital certificate issued under the electronic authentication system based on the commercial register) (Note 1) must be added after receiving an electronic contract without delay and a time stamp meeting a certain requirement (Note 2) shall be affixed.
(2) Regulations on administrative procedures for preventing the forgery of electromagnetic records regarding their maintenance shall be established, the administration procedures shall be implemented according to the regulations, and the relevant regulations shall be kept in the office.
(Note 1) It is expected that digital signatures will no longer be necessary following the planned revision of the tax laws this year.
(Note 2) The time stamp issued by a business operator who is certified under the accreditation program for time-stamping services conducted by Japan Data Communications Association
2. Electronic Submission
Previously, commercial and corporate registration required a procedure of going to the service counter of the relevant government agency, filling out forms with required items, and affixing a seal. This also applied to obtaining copies of resident registers, and the applicant (or his/her proxy) was required to visit the government agency and follow pre-defined procedures.
Electronic submission allows such administrative procedures-including filing or submitting applications, notifications, and reports-to be done electronically via the Internet, thereby reducing the amount of paper work and making it more convenient for companies and ordinary citizens.
- Among all services provided by government agencies, 3,768 types of submission procedures are available online (as of fiscal year 2013)
- Main electronic submission systems
e-Gov Electronic Submission System
Applications and notifications can be submitted to go through various administrative procedures under the jurisdiction of each government office. This is convenient when submitting applications and notifications to multiple government offices at once.
Online Registration and Deposit Application System
Applications for real estate registration, commercial and corporate registrations, movables assignment registration, assignment registration, deposits, adult guardianship registration, and electronic notarization can be made.
e-TAX System
Income tax, corporate tax, and consumption tax as well as liquor tax and stamp tax can be filed.
Electronic Patent Application Filing System
An application for industrial property rights can be filed with the Japan Patent Office.
Other electronic submission systems
* For details on electronic submission with each local government, check the respective websites
3. Electronic Bidding
Electronic bidding refers to going through procedures for bids hosted by the government and government agencies-i.e., from providing bidding information and distributing briefing documents to actual bidding, contracts, and authentication - electronically.
Due to the using IT for bidding systems promoted mainly by the national government and local governments, which have eliminated paper-based bidding in principle, electronic bidding systems that are highly utilized are spreading. In order to support seamless implementation of such systems to public ordering organizations, a versatile e-Bidding Core System, which multiple public ordering organizations can adopt, has been developed and used by the national government and local government offices.
In addition, with the Electronic Procurement System-which was launched in March 2014-a series of procurement procedures pertaining to "providing logistics support, supplies and services" and "some public works projects" hosted by the government, not only for tendering and opening a bid, but also other procedures including contact, delivery inspection, and billing are performed electronically. Contracts and other documents are maintained on the Electronic Procurement System. Organizations adopting this system are gradually increasing.
4. Secure / Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME)
Adding digital signature to e-mails can prevent authenticate a sender, and provides message integrity and non-repudiation. For example, financial institutions use this system extensively when sending e-mails to customers to prevent phishing. Although major e-mail software is equipped with a feature to send and receive S/MIME e-mail, using the feature requires an digital certificate enabling S/MIME digital signature.
In addition, with S/MIME, e-mails can be encrypted by using the digital certificate held by the other party.
5. Digital Archiving
Digital archiving of documents related to national tax or healthcare that are legally mandated to be stored may require adding digital signatures and time stamps, depending on the laws, guidelines, and other regulations. By using long term signature, the validity of the digital signature can be secured for a long period of more than 10 years.
As for national tax related documents, the Electronic Books Maintenance Act permits the scanning of paper-based transaction documents (with conditions) and these scanned documents can be archived as electronic files, with advance approval by the tax office (Note 3). For more information on the archiving of online electronic transactions, refer to Section 1. Electronic Contracts.
In addition, from the perspective of the legal obligation to archive documents, digital signatures and time stamps are added to electronic records concerning research and development before they are stored in some cases for the purpose of establishing the right of prior use in the area of intellectual property or in compliance with the Product Liability Act.
(Note 3) It is expected that digital signatures will no longer be necessary following the planned revision of the tax laws this year.
Service of Designated Investigative Organization
JIPDEC provides information provision, advice, and other support services in response to inquiries and consultation from entities conducting the Specified Certification Business, and the users of those services.